The Alliance for
Global Women’s Medicine
A worldwide fellowship of health professionals working together to
promote, advocate for and enhance the Welfare of Women everywhere
Menu
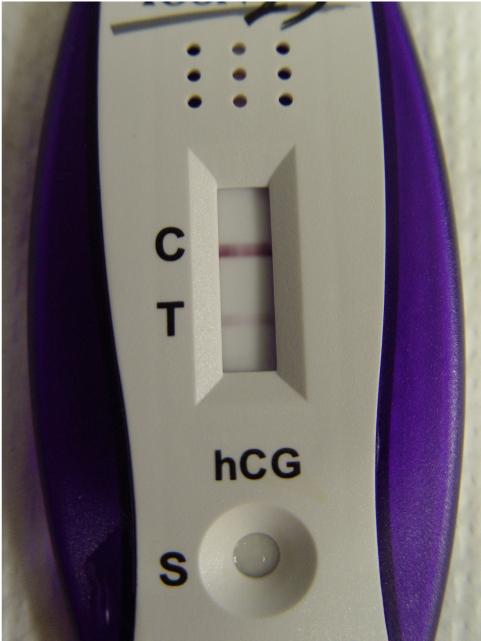
Pregnancy Test
|